Blog of Nursing Home Reviews in Chicago, Illinois
Have Nursing Homes Gotten Worse?
May 23, 2023

As the number of nursing home residents increases and society's elderly population swells, the demand for nursing homes and assisted living facilities has never been greater. However, despite the growing need, the American Health Care Association reports a troubling trend: a workforce crisis in the nursing home industry.
This dire situation threatens the quality of care for vulnerable residents, risking their safety. But how did we get here? And what can be done to address this crisis?
Causes of Workforce Crisis in Nursing Homes and Assisted Living Communities
The staffing crisis is fueled by several factors that have made it difficult for nursing centers and assisted living homes to retain and attract staff:
Low pay and inadequate benefits: Many nursing home workers struggle with low wages and insufficient benefits, particularly nursing aides. Research shows that competitive wages are essential for attracting and retaining qualified candidates.
High levels of burnout and stress among caregivers: Front-line workers often face intense physical and emotional demands, leading to high turnover rates and staff shortages.
Lack of training and professional development opportunities: Limited resources for training and development can exacerbate burnout and hamper staff retention.
Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic: The health care sector has been hit hard. Long-term care homes like nursing homes and assisted living communities face unique challenges in ensuring the safety and well-being of residents and staff.
Impact of Staffing Crisis on Nursing Homes and Assisted Living Communities
The staffing crisis has significant consequences for nursing homes and assisted living communities:
Quality of care and resident safety: Staffing shortages can compromise the quality of care for residents, putting their health and safety at risk.
Staff retention and turnover rates: Elevated job turnover rates can disrupt the continuity of care and hinder the ability of caregiving homes to maintain adequate staffing levels.
Financial implications: Recruiting and training new staff is costly, and many caregiving homes rely on temporary employees and staffing agencies to fill the gap, further straining their resources.
The Financial Strain on Assisted Living Centers and Nursing Homes
The staffing crisis has increased financial strain on assisted living centers and nursing homes. The American Health Care Association and National Center for Assisted Living (AHCA/NCAL) have raised concerns about the long-term sustainability of many caregiving centers due to the growing demand for competitive wages and the need for additional funding.
The actual cost of care: The healthcare sector faces the challenge of covering the cost of providing care for the nation's seniors. With the increasing demand for long-term care, facilities must find ways to balance their budgets while ensuring quality care for their patients.
Funding and reimbursement rates: The Kaiser Family Foundation has reported that funding for long-term care facilities has yet to keep pace with the growing demand, leading to a dire situation for many facilities that struggle to attract qualified candidates and retain staff due to low wages.
Contingency staffing: Many facilities have turned to staffing agencies and temporary workers in response to staff shortages, further exacerbating the financial strain on these organizations. Although a contingency workforce can help fill open positions, it often comes at a higher cost that negatively impacts the continuity of care for patients.
The Impact of Staffing Shortages on Rehabilitation Centers and Post-Acute Care
The nursing home providers crisis has significant implications for rehabilitation centers and post-acute facilities, as they, too, face staffing shortages. The American Health Care Association and National Center for Assisted Living (AHCA/NCAL) have emphasized the importance of addressing these issues to ensure that all care providers can meet patients' needs.
The ripple effect of staffing shortages: As nursing homes and assisted living facilities struggle to maintain adequate staffing levels, the burden often falls on rehabilitation center facilities. These facilities may experience an influx of fewer people seeking care as they need help to accommodate the increased demand caused by the staffing crisis in long-term care.
Managing the workload: To cope with the staffing shortages, many long-term care providers are forced to rely on their existing staff to pick up extra shifts and work overtime. While helpful in the short term, this approach can lead to increased burnout and high turnover rates among staff, further exacerbating the problem.
The American Health Care Association and the National Center for Assisted Living (AHCA/NCAL) are actively working to address the nursing shortage crisis in nursing homes and assisted living in rehabilitation centers and post-acute care facilities. By advocating for policy changes and increased funding, the AHCA/NCAL aims to support all long-term care providers in overcoming their staffing challenges.
By recognizing and addressing the impact of staffing shortages on rehabilitation centers and post-acute care facilities, stakeholders can ensure that these critical care providers can continue to offer high-quality services to their patients amid the staffing crisis.
The Role of the Senior Vice President in Addressing Workforce Challenges
Senior vice presidents of nursing home providers and assisted living facility operators are crucial in addressing the staffing crisis. Their leadership is essential in implementing strategies that prioritize long-term care and improve the quality of life for vulnerable patients.
Developing new admissions policies: In light of the workforce challenges, senior vice presidents can work on creating new admissions policies that ensure the needs of incoming residents are met and those facilities can adequately staff their operations.
Promoting increased wages and benefits: Senior vice presidents can advocate for increased wages and benefits for nurse's aides and other front-line workers, recognizing the importance of offering competitive compensation packages to attract and retain a dedicated workforce.
Advocating for more funding: By working closely with policymakers and industry leaders, senior vice presidents can push for more funding to support the long-term care industry, addressing the financial challenges facilities face in the wake of the staffing crisis.
The Importance of Research in Informing Long-Term Solutions
Research shows that evidence-based approaches are essential for developing effective long-term solutions to address the staffing crisis in skilled nursing facilities and assisted living communities.
Understanding the workforce's needs: Research can help identify the specific needs and challenges faced by nursing aides and other direct care staff, informing targeted interventions to improve job satisfaction, retention, and nursing home care quality.
Evaluating the impact of policies and programs: Rigorous evaluation of existing policies and programs can provide valuable insights into their effectiveness and inform the development of new, evidence-based strategies.
Informing the development of best practices: By studying successful interventions and innovative models of care, researchers can help identify best practices that facilities can adopt across the long-term care facility spectrum.
By leveraging the power of research, stakeholders can make informed decisions to address the staffing crisis, ensuring that nursing homes and assisted living centers are equipped to provide high-quality care for their residents now and in the future.
Solutions to Address the Workforce Crisis
To tackle the staffing crisis, nursing homes and assisted living centers must prioritize long-term solutions:
Increase pay and benefits for caregivers: Offering competitive wages and benefits can attract and retain a dedicated workforce.
Improve working conditions and reduce stress and burnout: Providing support, resources, and opportunities for growth can help alleviate burnout and improve staff satisfaction.
Invest in training and professional development opportunities: Continuing education and career development can enhance staff retention and improve care quality.
Implement policies and programs to attract and retain caregivers: Partnerships with educational institutions, targeted recruitment efforts, and innovative staffing models can help attract a skilled workforce.
Address the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic: Ensuring the safety and well-being of staff and patients will be crucial for rebuilding and sustaining the long-term care workforce.
A Call to Action
The staffing crisis in nursing homes is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention from policymakers, industry leaders, and other stakeholders. By prioritizing an effective long-term solution and investing in the nation's seniors, we can help ensure that all nursing home residents receive the high-quality care they deserve. The time for action is now.
Resources:
Can Bed Sores Kill a Nursing Home Resident
May 15, 2023
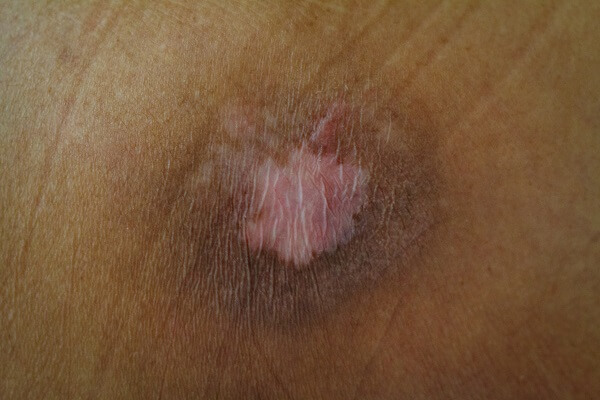
Bed sores (pressure ulcers) are a common and distressing issue plaguing countless nursing home residents. Often overlooked, these painful skin lesions can have devastating consequences if not properly addressed.
Pressure Ulcers in Nursing Homes
What are Bed Sores?
Bed sores, also known as pressure ulcers or decubitus ulcers, are injuries to the skin and underlying tissues caused by prolonged pressure on an area of the body. They are a common concern for residents, particularly those with limited mobility.
Importance of Discussing the Topic
Addressing the issue of bed sores is crucial, as they can lead to severe complications and even death if left untreated.
As our population ages, the number of elderly individuals residing in nursing facilities continues to grow, making it essential to understand the risks associated with bed sores and how to prevent them.
Statistics Regarding Bed Sores and Mortality
According to recent studies, approximately 2.5 million pressure ulcers occur in the United States annually, with an estimated 60,000 deaths yearly due to complications from these wounds.
It is essential to be informed about bed sores and their potential consequences to protect the well-being of our loved ones in nursing facilities.
Causes of Bed Sores
One of the primary contributing factors for developing bed sores is immobility. Elderly nursing home residents who are bedridden or use a wheelchair for extended periods are particularly susceptible to developing pressure sores, as they cannot shift their weight and relieve pressure on vulnerable areas of the body.
Friction and Shear
Friction and shear forces can also contribute to the formation of bed sores. When the skin rubs against bedding or clothing, it can become irritated and more susceptible to damage. Similarly, the skin can stretch and tear when the body slides against a surface, increasing the risk of pressure ulcers.
Incontinence
Incontinence is another common risk factor for bedsores, as the moisture and bacteria from urine or feces can irritate the skin and make it more prone to damage.
Poor Nutrition
Getting adequate nutrition is essential for maintaining healthy skin and promoting healing. A lack of essential nutrients can weaken the skin and increase the risk of developing bed sores.
Medical Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and vascular disease, can reduce blood supply to the skin, increasing the risk of skin ulcers.
Symptoms and Stages of Bedsores
Stage 1
In stage 1, the skin may appear red or discolored, feel warm to the touch, and not blanch (lighten) when pressed. The pressure sore is still superficial at this stage and can be reversed with appropriate treatment.
Stage 2
At this stage, pressure wounds damage the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and the underlying layer (dermis). The wound may appear shallow, open sore, or a fluid-filled blister.
Stage 3
The pressure ulcer extends into the fatty tissue below the skin at this stage, creating a deep, crater-like wound. Damage to the underlying tissues and possible infection may occur at this stage.
Stage 4
In Stage 4, pressure ulcers involve extensive damage to the skin, underlying muscle tissue, and sometimes muscle, bone, or joints. These severe wounds are challenging to treat and may require surgical intervention. At this stage, bed sores lead to death.
Complications of Bed Sores
Blood and Bone Infections
Infections are a common complication of bedsores after the skin breaks at the wound site. Typically, an open wound provides an entry point for bacteria, leading to developed bed sores. If nursing home negligence is a factor in improper wound care, the risk of severe infection increases.
Sepsis
In severe cases, an untreated bacterial infection can progress to sepsis (septic shock). In this life-threatening condition, the infection spreads throughout the body, potentially leading to organ failure and death.
Residents with bedsores must be closely monitored to prevent such bacterial infection complications.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can develop in the affected area around a bed sore. If not treated immediately, it can spread and cause further complications.
Bone and Joint Infections
Bedsores that reach the deeper tissues can cause bone infections (osteomyelitis) and joint infections (septic arthritis). These complications may arise from the assisted living facility or senior home's negligence in providing appropriate care.
Gangrene
In extreme cases, bedsores can lead to gangrene, which occurs when tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply. This serious condition may require amputation to prevent the spread of infection.
Can Bedsores Cause Death?
An estimated 60,000 deaths occur annually in the United States due to complications from bedsores. These sobering statistics emphasize the need for proper prevention and treatment in nursing homes and assisted living facilities.
Factors Contributing to Nursing Home Residents' Mortality
Several factors contribute to the increased risk of death from bedsores, including advanced age, underlying medical conditions, and lack of proper treatment. In some instances, nursing home abuse or negligence may also play a role.
Legal Implications of Bedsores and Death
A nursing home resident can die from bedsores. It is often determined that the nursing home's negligence caused the development or worsening of the sores.
When this occurs, the family may have grounds to sue a nursing home for damages, including medical bills and pain and suffering.
Bed Sore Prevention and Treatment
Steps that prevent bedsores include the following:
Skincare: Regularly inspecting the skin for early signs of bedsores and maintaining cleanliness can help prevent these wounds from forming.
Repositioning: Frequent position changes can reduce pressure on vulnerable areas and improve blood flow, helping to prevent pressure sores.
Nutrition and hydration: Ensuring nursing home residents receive proper nutrition and hydration is essential for maintaining healthy skin and promoting wound healing.
Exercise: Encouraging movement and exercise, when possible, can help maintain muscle tissue and reduce the risk of bedsores.
Appropriate treatment usually includes the following:
Wound care: Proper wound care, including cleaning and dressing the bed sore, is essential for promoting healing and preventing infection.
Medications: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections, while pain relievers and other medications may be used to manage symptoms and promote healing.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove dead tissue or repair the affected area.
Final Thoughts
The prevention and treatment of bedsores are critical for ensuring the health and well-being of nursing home residents. We can help reduce the risk of these painful and potentially life-threatening wounds through proper care and attention.
Continued research into bed sore prevention and treatment strategies is essential for improving the quality of life for nursing home residents and reducing the risk of complications.
By understanding the causes and risk factors, caregivers, medical professionals, and families can work together to ensure our loved ones receive the best care and support in their living facilities.
Resources:
Elderly Brain Bleed in Nursing Home
March 5, 2023

Brain injuries in nursing homes often result in severe consequences affecting many elderly residents. A brain injury can range from a mild concussion to a life-threatening head injury.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of injuries to the brain (cerebrum) in nursing homes is essential to prevent them from happening and ensure that victims and their families receive the support they need.
Identification of a Brain or Head Injury
A brain injury, also known as a head injury, is any damage to the cerebrum due to trauma to the head. It can include a blow to the head, a fall, or a car accident.
Injuries to the brain can range from mild, such as a concussion, to severe, such as a subdural hematoma brain bleed.
Causes of Brain Bleeds in a Nursing Home
Brain bleeds in a nursing home can be caused by various factors, including head injuries from slips and falls and abuse or neglect by nursing home staff.
Nursing Home Fall Injuries
Nursing home falls are a common cause of head injuries among residents. Of the 1.6 million residents in US nursing facilities, approximately half experience a nursing home fall annually. About one in three of those who have already experienced a nursing home fall will fall two or more times in a year.
Elderly residents may fall for various reasons, including:
Poor lighting in a nursing home facility
Slippery floors, snowy sidewalks, and icy areas
Tripping hazards, such as a loose carpet or loose floorboard
A nursing home resident's fall can result in head injuries, including subdural hematomas, which can seriously affect the health and well-being of elderly residents.
Elder Abuse or Neglect
Nursing home abuse or neglect is another common cause of subdural hematomas. Neglect can occur when nursing home staff do not provide adequate care and support to elderly residents. Nursing home abuse can happen when residents suffer intentional physical harm from nursing facility staff.
Nursing home abuse and neglect, leading to head injury, can include:
Failing to properly monitor residents with a high risk of falling
Not providing safe living conditions
Not administering adequate medical care
Physically manhandling residents by hitting, pushing, slapping, fisting, or causing them to fall in any way
Nursing home negligence and elder abuse can result in head injuries and other serious health complications for elderly residents.
How a Subdural Hematoma Occurs
Subdural hematomas occur when blood vessels burst in the space between the brain and the outermost membrane (dura mater). Blood collection forms a hematoma, which puts pressure on the brain tissue.
In nursing homes, subdural hematomas can result from falls, especially when residents are taking blood thinners. The buildup of blood can put pressure on the cerebrum and cause serious injuries and even death.
Types of Subdural Hematoma Brain Bleeds
Traumatic brain injury occurs when the cerebrum sustains an injury from a fall or a blow to the head
Ruptured blood vessels can occur due to a traumatic injury to the head
Bruised brain tissue can occur as a result of a traumatic head injury
Broken bones can result from a traumatic injury to the head caused by a blow to the head or a fall, resulting in brain swelling and additional damage to the cerebrum
Diffuse axonal injury occurs when the cerebrum is damaged due to rapid acceleration or deceleration, such as in a car accident or a fall
Acute subdural hematomas occur when a subdural hematoma is diagnosed within hours, days, or as long as two weeks after the traumatic injury or fall
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding in the spaces surrounding the brain, often resulting from a head injury, ruptured aneurysms, and other conditions
Injury to the outermost membrane or dura: a traumatic injury to the head is the cause, leading to bleeding and pressure on the brain
Understanding Subdural Hematoma Injuries in a Nursing Home
Subdural hematoma injuries are a type of brain injury that can result from a head injury. These injuries are caused by a buildup of blood between the brain and the skull, which can result in pressure on the cerebrum and other serious health problems.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of a subdural hematoma injury include headaches, confusion, and loss of consciousness. The diagnosis of a subdural hematoma injury is typically made through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and a review of the patient's medical history.
Brain Bleed Prevention
To prevent subdural hematoma injuries in nursing homes, it is vital to reduce the risk of falls and provide adequate care and support to elderly residents. It can include improving lighting, installing safety devices, using non-slip mats, and providing sufficient medical care.
Nursing home injuries especially falls, remain the leading cause of acute subdural hematoma in elderly nursing home residents.
With the increased risk of falls among nursing home residents and the prevalent use of blood thinners, nursing homes must provide proper care and fall prevention.
Brain Bleed Treatment
Patient falls can result in severe head injuries, including acute subdural hematoma. Early detection and prompt treatment of a subdural hematoma in older adults are essential to prevent serious complications or death.
If left untreated, a subdural hematoma can lead to a decline in cognitive and physical functioning, slurred speech, and other symptoms in a nursing home resident.
Treatment for subdural hematoma injuries may include surgery, medication, and rehabilitation. In severe cases, surgical drainage of the hematoma may be necessary to relieve the pressure it puts on the brain.
How a Personal Injury Lawyer Can Help in Elderly Brain Bleed Cases
A personal injury lawyer can help victims and their families in elderly brain bleed cases by holding the nursing home accountable and seeking maximum compensation for injuries of nursing home patients.
In nursing home falls resulting in a subdural hematoma, a personal injury lawyer can help hold the facility responsible for the injury, or death of a loved one. Personal injury lawyers represent nursing home neglect and abuse victims and can help families seek compensation for their losses.
Many law firms offer a free consultation to discuss the nursing home injuries or wrongful death of a loved one and determine the validity of a personal injury claim.
Resources:
How Long Can You Live in a Nursing Home?
February 25, 2023

As individuals grow older, their health needs may become more complex, often requiring extensive medical services and long-term care.
Many seniors need to move into a nursing home or assisted living facility to ensure their well-being. They rely on medical professionals' expertise and family members' support to navigate this transition.
About half of the residents have chronic conditions that require ongoing attention, making it essential to find a skilled nursing facility that provides high-quality care and comprehensive long-term care services.
Numerous contributing factors impact one's quality of life in this environment and how medical professionals and family members can work together to promote health and happiness for seniors in these settings.
How Long Does the Average Person Need Long-Term Care Services?
Concerning healthcare and aging, long-term nursing care services can become an essential part of one's daily life. The need for long-term services can arise due to chronic conditions, age-related limitations, and other healthcare issues.
About half of the residents have relocated to an assisted living facility or caregiving home for specialized medical services and care. It is estimated that almost half of nursing home residents require long-term services, making it crucial to find a facility that offers high-quality care to promote optimal health and well-being.
A long-term care home provides additional services not provided at an assisted living facility. the differences include:
Assisted Living Facility:
Provides personal care and support services, such as bathing and dressing assistance, medication management, and meals
Offers recreational/social activities to promote engagement and wellbeing
Typically suited for seniors who can live relatively independently but may need assistance with daily tasks
Often offers apartment-style living arrangements with some communal spaces
Usually does not offer 24-hour medical care on-site
Long-term Care Home:
Offers comprehensive medical and personal care to seniors with more complex health needs, such as chronic illnesses, disabilities, or memory loss
Provides around-the-clock nursing care, including medication management, wound care, and monitoring of vital signs
Offers a variety of therapies and treatments, such as physical therapy and occupational therapy
Typically provides communal living arrangements with private or shared rooms
Often includes specialized memory care units for residents with dementia or Alzheimer's disease
The Truth About Staying in Nursing Homes: 2019 Statistics on Reasons for Departure and Length of Stay
According to 2019 statistics, the average length of stay in caregiving homes was approximately 835 days.
However, the reasons for leaving nursing facilities vary widely, ranging from returning home after rehabilitation to living out one's life due to chronic medical issues, physical disabilities, or developmental/intellectual disabilities.
Understanding these reasons can help individuals and families make informed decisions about long-term care.
Reasons for Departure from Nursing Homes
Returning home after rehabilitation
Transitioning to assisted living or a more independent living arrangement
Living out one's life due to chronic medical issues or disabilities
Factors Impacting Length of Stay in Caregiving Homes
The severity of conditions or disabilities
Availability of family or support systems
Quality of care provided by the facility
Ability to pay for long-term nursing care
Do I Need Long-Term Care or Assisted Living Care?
As individuals age, their health needs may become more complex, requiring specialized care and support to maintain a good quality of living. Assisted living and long-term care are options for many seniors that can provide the necessary care to meet their unique needs.
Choosing between the two can be difficult, requiring careful consideration of personal preferences, health status, and family support. Both types of care offer different levels of assistance and support, so it is vital to understand the differences and benefits of each.
How Much Does Long-Term Care Cost?
Long-term care costs are a significant concern for many seniors and their families. As individuals grow old, their health needs may become more complex, requiring specialized medical care and support.
The cost of professional care can be substantial, making it essential to understand the options and factors impacting long-term care costs. Understanding how much long-term nursing care cost, the various factors impacting costs, and the resources available to help individuals and families cover these expenses.
According to 2019 statistics, the average length of stay in caregiving homes was approximately 835 days. However, the reasons for leaving nursing facilities vary widely, including returning home after rehabilitation to living out one's remaining days due to chronic health issues, physical disabilities, or developmental/intellectual disabilities.
According to 2019 statistics, the average cost of a nursing facility stay in the United States was approximately $7,500 per month or $90,000 per year. Long-term care costs can vary widely depending on various factors, such as the location of the facility and the level of care required.
Here are some additional statistics and factors to consider when it comes to the cost of nursing home stays:
The cost of care can range from $5,000 to $10,000 per month, depending on the level of care required
Medicaid can help cover the cost of long-term care services for eligible individuals, but coverage and eligibility requirements vary by state
Long-term care insurance can provide additional financial support for those who need long-term nursing care, but policies can be expensive and may have limitations or exclusions
Understanding the cost of long-term care can help individuals and families plan for the future and make informed decisions about their healthcare needs.
Resources:
Is Sepsis a Sign of Poor Nursing Home Care?
February 22, 2023

While nursing homes can provide a safe and supportive living environment for seniors, there are risks associated with this type of care. One of the most severe risks is the development of sepsis, a life-threatening condition resulting from poor nursing home care.
Sepsis is a medical emergency when the body's immune system overreacts to an infection. Sepsis can cause organ failure, septic shock, and even death if not treated promptly.
Nursing home residents are particularly vulnerable to sepsis due to age, chronic medical conditions, and compromised immune systems. In addition, close living quarters and poor hygiene practices can lead to a higher risk of infection.
The Alarming Connection Between Nursing Home Deficiencies and Sepsis in Residents
Nursing home sepsis is a significant concern for many residents and their families. According to data from federal and state agencies, sepsis is one of the leading causes of hospitalization and death in nursing home residents.
According to Kaiser Health News, sepsis is responsible for over 1.7 million hospitalizations and 270,000 deaths yearly, with a mortality rate of around 15-30% nationwide. Studies show that sepsis is one of the top ten reasons for hospital transfers among elderly patients, and it is responsible for up to 40% of deaths in this population.
The Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH) has reported that sepsis is the third most common cause of death in Illinois nursing homes, following dementia and heart disease.
In 2019, there were 6,268 reported cases of sepsis in Illinois nursing homes, resulting in 1,352 deaths. This statistic represents a significant increase from the previous year when there were 5,510 cases of sepsis and 1,156 deaths.
The IDPH has also reported that nursing homes with a higher number of deficiencies are more likely to have cases of sepsis.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) also collects data on nursing home and assisted living facility sepsis rates as part of the Nursing Home Compare program. According to CMS, in 2020, around 4.5% of long-term care residents had sepsis, and around 12% of short-stay residents had sepsis.
The overall sepsis survival rate is around 75%. Severe sepsis develops at a lower rate than septic shock. Furthermore, CMS data shows that nursing facilities with a lower rating on the Five-Star Quality Rating System are more likely to have higher sepsis rates.
Avoidable Sepsis Infections
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), many cases of sepsis in nursing homes are avoidable with proper infection control measures, prompt treatment of infections, and adequate staffing levels. However, nursing home negligence can increase residents' sepsis risk.
By understanding sepsis statistics and working to prevent avoidable infections, we can help protect patients and ensure they receive the quality care they deserve.
What is Sepsis, and How Does it Develop in Nursing Home Residents?
Sepsis is a severe medical condition when the body's inflammatory response overreacts in the immune system leading to an infection. It can cause organ damage, septic shock, and even death.
Severe sepsis occurs when sepsis has progressed to organ or tissue damage, while septic shock is the most severe form of sepsis, where the patient's blood pressure drops to dangerously low levels.
Conditions where patients develop sepsis and septic shock that may lead to death include:
Bacterial infections, such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections
Fungal infections, such as candida or aspergillosis
Viral infections, such as influenza or COVID-19
Parasitic infections, such as malaria or Leishmaniasis
Medical malpractice, such as misdiagnosis or delayed treatment of infections
Low blood pressure or septic shock resulting from sepsis
Poor infection control practices, including inadequate cleaning and disinfection of medical equipment and facilities
Lack of prompt medical care and intervention, including delayed administration of antibiotics or other treatments
Pressure ulcers, bedsores or open wounds, which can become infected and lead to sepsis
Restricted blood flow or tissue damage in bedridden patients resulting from conditions such as deep vein thrombosis or gangrene
Infections related to weakened immune systems
In particular, urinary tract infection (UTI) is a severe medical condition in older adults in assisted living facilities and nursing caregiving homes. It can lead to sepsis infection if untreated or not treated promptly.
Risk Factors for Developing Sepsis in Nursing Homes
Several risk factors can increase a resident's risk of developing deadly sepsis. These include advanced age, chronic medical conditions, weakened immune systems, and previous hospitalizations. Additionally, caregiving patients may be more susceptible to infections due to close living quarters and the potential for poor hygiene practices.
Sepsis as a Sign of Nursing Home Neglect and Abuse
Neglect can occur when staff members fail to provide adequate care and attention to residents. It can include not properly monitoring for signs of infection, failing to provide necessary health care, and not maintaining proper hygiene practices.
Neglect can increase a resident's risk of developing sepsis and signify more significant nursing home issues.
Identifying the Signs of Abuse
Sepsis in nursing homes can also signify abusive behavior, which occurs when a staff member intentionally harms a resident. Signs of abuse can include unexplained injuries, sudden changes in patient behavior, and frequent illnesses.
If you suspect neglect or abuse is occurring, you must contact a personal injury lawyer immediately.
The Importance of Immediate Treatment for Sepsis in Nursing Facilities
Early detection of sepsis is critical for a positive outcome. Nursing staff should be trained to recognize the signs of sepsis, including fever, rapid breathing, increased heart rate, and a sepsis rash.
If a nursing home resident exhibits sepsis symptoms, they should receive immediate medical attention.
Treating Sepsis in Nursing Home Patients
Once sepsis occurs, immediate care is essential. This care can include antibiotics, intravenous fluids, and other supportive measures. In severe cases, the resident may require critical care medicine or hospitalization.
However, preventing sepsis infections from occurring is the best approach through proper infection control measures and prompt treatment of infections.
Is a Lack of Proper Medical Care a Sign of Nursing Home Negligence?
Sepsis is a sign that something has gone wrong, and it can be an indication of abuse or neglect. Neglect can occur when nursing home staff members fail to provide residents with adequate care, attention, and supervision.
It can include not monitoring for signs of infection, failing to provide necessary medical treatment, and not maintaining proper hygiene practices.
How a Nursing Home Abuse Lawyer Can Help | Free Consultation
If you or a family member developed sepsis due to nursing home abuse or neglect, it is essential to contact a personal injury lawyer. These legal professionals represent nursing facility patients and their families and can help you understand your legal options, including filing a nursing home sepsis lawsuit.
Building a Nursing Home Abuse or Neglect Case
A lawyer can also help you build a strong case for nursing home abuse or neglect. They can investigate the nursing home's practices, gather evidence, and work with medical experts to prove that the facility was responsible for your loved one's sepsis.
With the help of an experienced lawyer, you can hold the nursing home accountable for their actions and seek the compensation you and your loved one deserve. All surviving family members can file wrongful death lawsuits for compensation.
All confidential information shared remains private through an attorney-client relationship.
Resources:
Damages in Nursing Home Lawsuit
February 18, 2023

As the population ages, more individuals need nursing homes and assisted living facilities to provide proper medical care and assistance with daily living activities.
Unfortunately, nursing home abuse and negligence have become a severe concern in the United States. Statistics indicate that around one in 10 nursing home residents have experienced abuse.
When nursing home staff members fail to provide medical care, elderly individuals can suffer severe injuries and illnesses, resulting in significant medical bills and other significant damages, including pain and suffering.
Understanding Abuse and Negligence
Nursing homes and assisted living facilities provide critical care and support for elderly individuals who can no longer live independently.
However, when staff members fail to provide care and support to a nursing home resident, it can lead to severe injuries and illnesses, including abuse and neglect.
Abuse and Neglect in a Nursing Home or Assisted Living Facility
Abuse can take many forms, including physical abuse, emotional abuse, sexual abuse, financial exploitation, and neglect. Physical abuse can involve hitting, pushing, or restraining residents, while emotional abuse can involve intimidation, humiliation, or isolation.
Sexual abuse can include unwanted touching or sexual assault, while financial exploitation can involve theft or fraud.
Nursing home negligence can include failure to provide proper care, food, or shelter, resulting in serious injury or illness.
Nursing Facility Abuse Statistics and Their Implications
A national survey shows approximately one in 10 nursing home patients have experienced abuse. However, due to underreporting and a lack of transparency in nursing homes, the actual prevalence of abuse and neglect may be even higher.
Abuse can result in serious injuries, illnesses, and even nursing home wrongful death. Individuals and their families must understand the implications of abuse statistics and take action to prevent future abuse.
While nursing abuse statistics are troubling, it is essential to note that they only represent a fraction of the cases of nursing home neglect and abuse. Individuals and their families must seek legal help if they suspect abuse, as it can result in severe injuries and preventable death.
Working with experienced personal injury attorneys can help victims, and their families obtain compensation through nursing home abuse settlements and ensure that nursing facility staff members are held accountable for elder abuse.
To build a case, nursing home lawyers gather the tools needed to fight for their clients and ensure they receive proper compensation for their suffering. A reputable lawyer will offer a free legal case review to discuss what happened.
Nursing Home Settlements - Understanding the Financial Compensation for Victims and Their Families
Monetary compensation through nursing home settlements can provide much-needed relief for victims and their families after experiencing abuse or neglect.
Examples of recent nursing home lawsuit settlements in the US:
Genesis Healthcare (Andover, Massachusetts) - September 2020 - $53 million nursing home neglect settlement over allegations of substandard care.
Consulate Health Care (Jacksonville, Florida) - January 2020 - $39 million nursing home lawsuit jury verdict for negligence resulting in serious injuries and preventable death.
The Ensign Group (Orange County, California) - November 2019 - $17 million nursing home neglect settlement over allegations of improper billing and substandard care.
SavaSeniorCare (Atlanta, Georgia) - June 2019 - $1.25 million nursing home lawsuit settlement over allegations of wrongful death due to inadequate care.
Life Care Centers of America (Cleveland, Tennessee) - February 2019 - $145 million personal injury lawsuit settlement offer over Medicare fraud and substandard care allegations.
HCR ManorCare (Toledo, Ohio) - September 2018 - $100 million nursing home lawsuit settlement over Medicare fraud and substandard care allegations.
Golden Living (Plano, Texas) - July 2018 - $613 million nursing home lawsuit settlement over allegations of improper billing and substandard care.
Consulate Health Care (Maitland, Florida) - May 2018 - $3 million nursing home litigationjury verdict for negligence resulting in severe injuries.
Life Care Centers of America (Cleveland, Tennessee) - March 2018 - $10 million settlement agreement over Medicare fraud and substandard care allegations.
Life Care Centers of America (Cleveland, Tennessee) - February 2018 - $16.7 million settlement offer over Medicare fraud and substandard care allegations.
Symphony Residences of Lincoln Park (Chicago, Illinois) - August 2019 - $1.25 million settlement over allegations of elder abuse when the nursing home failed to provide proper care leading to the death of a resident.
Alden Wentworth Rehabilitation and Health Care Center (Chicago, Illinois) - December 2018 - $1.5 million Illinois nursing home settlement over allegations of negligence resulting in the development of a pressure sore and infection in a resident.
Aperion Care Capitol (Springfield, Illinois) - July 2018 - $750,000 nursing home lawsuit settlement over allegations of negligence resulting in the development of multiple pressure ulcers in a resident.
How Personal Injury Lawyers Can Help Negotiate Nursing Home Settlements
Nursing home abuse attorneys are experienced in handling cases of neglect and abuse. Nursing home litigation that has led to negligence or abuse cases include:
Medication errors when the nursing home staff failed to follow drug administration protocols.
Medical malpractice occurs when residents are injured due to inadequate medical treatment or misdiagnosis. Medical negligence can lead to severe injuries.
Pressure sores and other injuries resulting from neglect and lack of proper care.
Physical abuse by staff or other residents, resulting in broken bones or other injuries.
Sexual abuse by staff or other residents, resulting in emotional trauma and physical injury.
Financial exploitation, including theft or fraud, by staff members or others.
Neglecting basic needs, including food, water, and hygiene, leads to serious illness or injury.
Failure to monitor and prevent falls or other accidents, resulting in severe injuries.
Staff members failing to provide adequate support leads to severe injuries or wrongful death.
Falls that lead to a brain injury, spinal cord damage, or fractured bones
The Role of a Personal Injury Attorney
An attorney can provide valuable legal guidance and support for individuals and their families who have experienced abuse. They can help you gather evidence, review medical records and build a strong nursing home abuse case. Many will offer a free consultation.
The Benefits of Hiring an Experienced Attorney
When pursuing legal action for abusive behavior, it is critical to work with an experienced attorney who understands the complexities of these cases.
An experienced attorney can help you negotiate nursing home settlement agreements and represent you in court, ensuring you receive the compensation you deserve. They can also provide emotional support and guidance throughout the legal process, helping you and your loved ones move forward.
The Legal Process for Nursing Home Lawsuit Settlements
Nursing home lawsuit settlements can be complex and lengthy, involving multiple parties and legal strategies.
The Different Types of Damages in Nursing Home Lawsuits
When pursuing legal action in a nursing home abuse case, victims and their families may be eligible for different damages.
Compensatory damages compensate victims for their financial losses, including medical costs, lost wages, and pain and suffering. Punitive damages may also be awarded in cases of gross negligence or intentional harm.
Settlement Negotiations and Average Settlement Amounts for Nursing Home Lawsuits
Many nursing home abuse lawsuits are resolved through claim negotiations rather than going to trial. In nursing home abuse settlement negotiations, both parties agree on a monetary compensation amount to resolve the case.
The average nursing home settlement amount varies widely depending on the case's specific circumstances but can range from thousands to millions of dollars. An experienced nursing home abuse lawyer can help you negotiate a fair settlement amount and protect your legal rights.
Compensatory and Punitive Damages in Nursing Home Lawsuits
Compensatory and punitive damages are critical considerations in nursing home lawsuit settlements.
Compensatory Damages for a Nursing Home Lawsuit Settlement
Compensatory damages in a nursing home abuse settlement are designed to compensate victims for their financial losses, including medical costs, lost wages, and pain and suffering.
These damages can help victims, and their families move forward after a traumatic experience and receive the medical treatment they need to recover.
Punitive Damages in Nursing Home Lawsuits and Their Purpose
Punitive damages in personal injury lawsuits are designed to punish the nursing home for their actions and deter similar behavior. Punitive damages may be awarded in cases of gross negligence or intentional harm and can result in a significant financial penalty for the nursing home.
Wrongful Death Settlements Involving Abuse and Neglect
In some abuse cases, victims may suffer an avoidable death. The family of the victim can file a compensation claim to negotiate a wrongful death settlement for damages.
Filing a Wrongful Death Lawsuit for Nursing Home Abuse
If a loved one has suffered an unexpected death due to abuse, it may be possible to file a civil lawsuit. Nursing home lawsuit settlements can help provide monetary compensation for medical costs, funeral expenses, and the emotional pain and suffering of the victim's family.
Nursing Home Settlement Amounts for Preventable Deaths
The nursing home abuse settlements can vary widely depending on the case's specific circumstances. An experienced nursing home abuse lawyer can help you negotiate a fair wrongful death settlement amount on behalf of your loved one.
Seeking Legal Help for Nursing Home Neglect and Abuse
Seeking legal help for nursing home negligence and abuse is essential for victims and their families to obtain monetary compensation and prevent future abuse.
How a Nursing Home Resident Can Find and Hire a Personal Injury Attorney
Finding and hiring a nursing home abuse attorney can be daunting. Working with an experienced lawyer who understands the complexities of nursing home abuse cases and can provide valuable legal guidance and support is essential.
Reputable law firms will provide a free case review to understand what happened and help you file a nursing home abuse lawsuit.
Resources:
How Many People Live in Nursing Homes
February 17, 2023

As we age, our health and independence become more fragile, and some seniors require additional support to maintain a high quality of life. While many elderly citizens prefer to live independently for as long as possible, others may require specialized long-term care services.
It is where nursing home centers and assisted living facilities come into play, providing round-the-clock care and support to those who need it.
Nursing Home Statistics: Understanding the State of Long-Term Care in the United States
Nursing homes are vital in providing long-term care services for those requiring specialized support and assistance. Here are some statistics on nursing home residents:
As of 2021, there are over 15,000 nursing home centers in the United States, providing care for more than 1.3 million residents.
Most nursing home residents are over 65 years old, and the age group of 85 and older is the most likely to live in nursing home centers.
Females tend to live longer, require more long-term caregiving services than men, and make up the majority of nursing home residents.
The number of nursing home residents with Alzheimer's, dementia, and memory loss is expected to increase as the population continues to age.
Nursing home centers have been particularly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. there were over 131,000 deaths among nursing home residents and staff as of December 2021.
While caregivers face challenges in providing high-quality care and support for their nursing home residents, they play a critical role in serving adults who require long-term services.
It is essential to ensure that the administration and nursing staff are held accountable for providing adequate care and preventing abuse and neglect to protect the well-being of their nursing home residents.
The Nursing Home Population
The number of nursing home residents has been steadily increasing, with a significant portion of the elderly population residing in nursing home centers.
The demand for long-term services will only grow as our population ages. It is estimated that by 2050, the number of people living in nursing home centers and assisted living facilities will double.
The populated nursing home industry comprises children and adults from various age groups who require long-term nursing services. Most nursing home residents are over 65 years old, and the number is expected to increase as the population ages.
Nursing home centers and assisted living communities provide community living for those requiring specialized care and support, with options for private and semi-private rooms.
These facilities serve both men and women, and there is a growing focus on providing person-centered care that caters to each individual resident's unique needs and preferences.
The Social Connection Between Assisted Living Residents
Assisted living communities offer an alternative option for those who require long-term caregiving services but desire more independence. Assisted living residents are younger than nursing home residents and often live in semi-private rooms.
While the cost of living in assisted living facilities can be lower than in nursing home centers, it still remains a significant expense for many individuals and their families.
However, assisted living centers can provide a social connection for residents, with various activities and events organized to encourage socialization and engagement. The number of assisted living facilities has been increasing in recent years, reflecting the growing demand for long-term services prioritizing quality living.
Cost of Living in Nursing Homes and Assisted Living Facilities
Nursing homes are more expensive than assisted living communities due to the higher level of care provided.
For both nursing homes and assisted living centers, the cost of private accommodations is typically higher than a semi-private room, and the cost of living can be affected by additional services such as physical therapy or specialized care for Alzheimer's, dementia, and memory loss.
Living in nursing homes and assisted living communities can be a significant expense for many families. Here are some key points to consider when thinking about the cost of long-term care:
The average monthly cost of a private room in a nursing home can range from $7,000 to $8,000, while a semi-private room can cost around $6,000 to $7,000 per month.
The cost can vary depending on the level of care nursing home residents require and the facility's location.
Additional services such as physical therapy or specialized care for Alzheimer's, dementia, or memory loss can increase the cost for nursing home residents and their families.
Women tend to require more long-term nursing services than men and may face a greater financial burden.
The age group of 85 and older is the most likely group to live in nursing homes.
Nursing homes and assisted living communities serve adults who require specialized care and support, providing a safe and comfortable living environment for those who live in nursing homes.
When considering long-term care options, it is essential to research and compare the costs of different facilities to find the best option for nursing home residents and their families. Other options are available to help cover these expenses, such as Medicaid and long-term care insurance.
Services Provided in Nursing Homes and Assisted Living Facilities
Nursing homes and assisted living communities offer a wide range of services to meet the needs of their residents. Some long-term care provided in nursing homes and assisted living centers includes:
Assistance with daily activities such as bathing, dressing, and grooming
Medication management and administration
Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy
Meal preparation and dietary management
Housekeeping and laundry services
Social and recreational activities, including outings and events
24-hour monitoring and assistance
Long-term care group home options based on a similar age group
While the services provided in nursing homes and assisted living facilities are similar, nursing homes tend to offer a higher level of medical care, while assisted living communities prioritize the resident's independence and self-care abilities.
Both types of facilities aim to provide person-centered care that meets each resident's unique needs and preferences.
The number of nursing homes and assisted living facilities is growing, with an increasing focus on providing person-centered care that prioritizes residents' well-being. Women require more long-term care than men and make up most nursing home residents.
As the population ages, it is essential to provide accessible and high-quality long-term care to support the seniors' needs.
Alzheimer's Disease and Other Dementias
Alzheimer's, memory loss or dementia are prevalent among the elderly and require specialized care. Below are some of the services provided by nursing homes and assisted living facilities for residents with Alzheimer's, memory loss, or dementia:
Secured environments that prevent assisted living residents from wandering and provide a safe living environment
Memory care programs that provide specialized support and therapies for those with Alzheimer's and other memory loss conditions
Social and recreational activities that promote engagement and cognitive stimulation
Training for nursing home staff to understand the unique needs and behaviors of those with dementia
Caring for Alzheimer's patients who live in nursing homes can be challenging, requiring specialized knowledge and support. However, nursing home centers and assisted living facilities are vital in providing care and support for those with these conditions.
Research shows that specialized programs and therapies can improve the lives of those with dementia.
As the population ages, the number of nursing home residents with Alzheimer's, memory, or dementia is expected to increase. It is essential to provide high-quality care and support for these individuals to ensure they can live as independently and comfortably as possible.
How a Nursing Home Abuse Lawyer Can Help
Nursing home abuse is a serious issue that can devastate residents and their families. Here are some ways an elder abuse lawyer can help those who live in nursing homes:
Investigating claims of abuse or neglect and gathering evidence to support legal action
Filing lawsuits on behalf of victims of abuse or neglect
Negotiating settlements with nursing facilities or other responsible parties
Ensuring that victims receive the compensation they deserve for medical bills, pain and suffering, and other damages
Holding nursing homes accountable for providing adequate care and preventing abuse and neglect in the future
If you suspect that your loved one is the victim of nursing home abuse, it is essential to take action to protect their rights and well-being. A nursing home abuse lawyer can provide the legal guidance and support you need to pursue justice and ensure that your loved one receives the care and compensation they deserve.
Resources:
How Long Does It Take for Bed Sores to Develop?
February 14, 2023

Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, can become a significant concern for nursing home residents who spend most of their time in bed or a chair. These painful injuries occur when constant pressure is placed on the skin, leading to damage in the underlying tissues and disruption of blood to the affected area.
If left untreated, pressure sores can result in the development of dying tissue and slow down the healing process. Medical professionals and caregivers need to understand the risk of developing bed sores to identify the signs before they become severe.
Bed Sore Statistics in the United States
In 2019, it was estimated that approximately 2.5 million people in the United States developed bed sores. This significant number highlights the importance of proper skincare and sore prevention measures to minimize harm to every nursing home resident.
What Is a Bed Sore and How Does it Develop?
Bed sores are injuries that develop on the skin and underlying tissues due to prolonged pressure on the affected area. They typically occur in elderly individuals, particularly those who are immobile and spend long periods of time in the same position.
The pressure interrupts the blood flow and circulation to the wounded area, which can result in the breakdown of healthy skin and the development of open wounds.
Three contributing factors to the development of bed sores are sustained pressure on the skin's surface, friction as the skin rubs against bedding or clothing, and shear as the skin is pulled across a surface.
To prevent bed sores in nursing home residents, healthcare professionals recommend regularly changing the patient's position, using a raised bed to relieve pressure, and ensuring that the patient's skin stays clean and dry.
If left untreated, bed sores can cause elderly residents significant pain and compromise their immune system, making them more susceptible to blood poisoning, joint infections, and necrosis, where the affected skin dies from a lack of blood flow.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Bedsore?
The development of a pressure sore in a nursing home resident can happen quickly, in a matter of hours or days, and depends on various factors. Prolonged pressure on the skin and underlying tissue can lead to damage in blood circulation, which can eventually cause the skin with little to no blood supply to die off.
In the early stages of a pressure ulcer, the wound may appear with reddened skin that doesn't turn white when pressed. Without treatment, pressure sores can develop quickly and progress through the entire thickness of the skin, affecting bony areas like the hips and heels.
At advanced stages, the skin eventually dies and turns black, increasing the risk of severe complications like septic arthritis and skin cancer. To prevent pressure sores, nursing home facilities must provide proper skincare and regularly change the resident's position to relieve pressure on boney areas.
Medical care can help heal early-stage pressure sores and prevent further complications from arising.
Treating Life-Threatening Bed Sores and Surrounding Tissue Damage
Bed sores can be life-threatening for nursing home residents when the surrounding area becomes damaged. Once a pressure ulcer has reached an advanced stage, it may require specialized treatment to prevent the spread of infection and further tissue damage.
Effective Treatment for Bed Sores
Effective treatment for bed sores includes keeping the wound clean and dry, using dressings to protect the wound, and managing pain with medication. In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the dead tissue and promote the growth of new, healthy tissue.
Pressure Sore Symptoms
Bed sores can cause significant discomfort and pain for nursing home residents. The first signs of a pressure sore may include redness or discoloration of the skin, which may not turn white when pressed. Without treatment, the sore may form a blister or ulcer that can become infected.
To prevent the development of pressure sores, nursing home facilities must take preventative measures such as changing the resident's position regularly and using unique beds that minimize bed pulls.
It's also essential to keep the resident's skin clean and dry, especially for darker skin, as they are more prone to developing bed sores. If a pressure sore is suspected, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately to prevent further tissue damage and the spread of infection.
How Do These Bedsores Develop in a Nursing Home?
Bed sores are common in nursing home residents due to various factors. For example, disabled and elderly residents with spinal cord injuries or mobility issues are more susceptible to developing pressure sores.
These injuries often occur in areas of the body that cover bony areas, such as the hips, heels, and shoulder blades, where there is less cushioning to protect the skin.
To prevent the development of pressure sores, nursing home facilities must follow sore prevention protocols such as changing the resident's position regularly and using special beds that minimize bed pulls.
It's also essential to ensure that residents receive proper nutrition and hydration and maintain proper skin care. Without intervention, pressure sores can progress to advanced stages where the skin will eventually die off, leading to severe complications such as infections and even death.
Common Pressure Ulcer Sites
Bed sores can develop on any body part that experiences ongoing pressure, friction, or shear. However, some areas of the body are more prone to developing pressure sores than others.
In elderly nursing home residents, pressure sores are commonly found in areas that cover bony areas, including:
Hips
Heels
Shoulder blades
Buttocks
Lower back
Elbows
Back of the head
Ankles
Knees
Behind the ears
Anyone with a severe spinal cord injury may also develop pressure sores on the buttocks or lower back.
To prevent the development of pressure wounds in a nursing home facility, the staff must ensure mobility-challenged residents change position regularly and use pressure-relieving air mattress beds that minimize friction.
It's also essential to ensure that residents receive proper nutrition and hydration and maintain proper skin care. Nursing home residents can minimize the risks of developing painful and potentially life-threatening bedsores by taking these steps.
What Are the Risk Factors for Pressure Ulcers?
Bedsores are a common concern for nursing home residents who spend long periods in bed or a chair. These painful injuries occur when constant pressure is placed on the skin, leading to damage in the underlying tissues and disruption of blood supply to the wound.
Without skin care intervention, decubitus ulcers can result in the development of dead tissue and slow down the healing process.
Severely Damaged Skin from Developing Bedsores
When pressure ulcers develop, they can quickly progress to severe stages without immediate intervention. The open wound can become infected, leading to dying tissue that can be difficult to heal. Damaged skin can lead to slower healing times and increase the risks of developing further pressure sores.
Nerve Damage
Individuals with nerve injuries due to spinal cord injuries or other conditions are at a higher risk of developing pressure ulcers. The damage can make detecting early signs of pressure sores more difficult, as the individual may not experience the same pain or discomfort that would usually signal a problem.
It's important for nursing home facilities to monitor residents with nerve injury closely and follow preventative protocols to reduce the risk of developing pressure ulcers.
Holding Nursing Home Facilities Accountable for Preventable Bedsores
Did you or a loved one experience preventable bed sores in a nursing home? There are legal options available to hold the facility accountable.
A personal injury lawyer can help you seek compensation for damages and ensure that the facility takes the necessary steps to prevent future occurrences of pressure ulcers.
By working with an experienced lawyer, you can help protect the rights of nursing home residents and improve the standard of care in these facilities.